Melatonin
Melatonin is a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles, used as a supplement to improve sleep quality and treat insomnia.
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland that helps regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
As a supplement, it supports sleep onset, jet lag recovery, and overall circadian rhythm balance.
Melatonin is generally safe for short-term use and is popular in sleep aids and nighttime wellness products.
Other names & forms of Melatonin supplement : n-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine, sleep hormone, melatonin supplement
Possible Benefits
As a circadian regulator, Melatonin delivers sleep quality and nightly recovery benefits:
- Helps support Sleep Support by reducing sleep latency and improving sleep quality.
- May aid Nervous System & Stress Relief through its anxiolytic effects that calm the mind before bedtime.
- Contributes to General Health by regulating the sleep-wake cycle, which is critical for immune function and metabolic balance.
Side Effects
Melatonin regulates sleep-wake cycles, but during initiation some users experience mild effects. Watch for:
- Temporary drowsiness extending beyond desired sleep period
- Occasional vivid dreams or nightmares
- Possible headache or dizziness on waking
- Rare gastrointestinal upset, nausea or cramps
- Very mild changes in sleep pattern irregularity with overuse
Interactions
Possible interactions include:
- Sedative and sleep aids: Melatonin’s sleep-promoting effects may combine with Valerian or prescription sedatives; monitor next-day drowsiness.
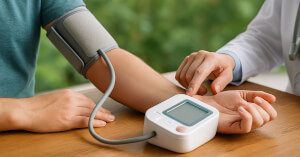
- Blood pressure medications: May slightly lower blood pressure; if used with ACE inhibitors, check vitals.
Precautions
Before taking Melatonin, confirm none of the following apply to you. If they do, consult your healthcare provider:
- Individuals on anticoagulants: Potential interactions; monitor bleeding risk
- People with autoimmune diseases: Melatonin may modulate immunity; use cautiously
- Those with depression: Possible mood alterations; consult psychiatrist
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Limited safety data; avoid high doses
- Patients scheduled for surgery: Discontinue at least one week prior, possible anesthesia interactions
Studies
These studies provide scientific insights into Melatonin benefits:
A 2013 meta-analysis of 19 RCTs found melatonin significantly reduced sleep onset latency by 7.9 minutes and improved total sleep time by 8.1 minutes versus placebo in primary insomnia.
A 2000 double-blind RCT in 60 elderly insomniacs showed 2 mg controlled-release melatonin for 4 weeks increased sleep efficiency by 12 % and total sleep time by 24 minutes versus placebo.
A 1987 crossover study of 0.5 mg melatonin versus placebo in 20 airline cabin crew flying eastward demonstrated reduced subjective jet‐lag scores and improved daytime alertness.
A 2000 randomized trial in 35 Alzheimer’s patients found 5 mg melatonin nightly for 12 weeks improved sleep efficiency by 14 % and reduced nocturnal awakenings versus placebo.
Disclaimer: This page is for educational purposes and does not replace medical advice. If you're pregnant, have a condition, or take medication, speak with a qualified professional.